Facing global health challenges, anthropological perspectives open doors to a deeper understanding of how human culture and social dynamics play a pivotal role in the spread of diseases, responses to pandemics, and recovery efforts.Anthropology teaches us that every society possesses unique health practices, reflected in belief systems, habits, and local traditions. When addressing global disease outbreaks, it is crucial to comprehend and respect these differences. How health and healing concepts are articulated in different cultures can impact the effectiveness of health interventions.
Anthropology delves into the social and economic impacts of pandemics at both local and global levels. How the social and economic structures of communities influence the spread of diseases, access to healthcare, and the capacity to recover. Anthropological research helps identify community vulnerabilities and design solutions centered around social justice.

In the context of global health, compliance with health protocols often depends on cultural and societal behaviors. Anthropology aids in analyzing how cultural norms and value systems influence the acceptance or rejection of preventive measures. This is crucial to optimize the effectiveness of health interventions.
Anthropology emphasizes the importance of involving local communities in the planning and implementation of global health programs. This involvement ensures that proposed solutions align with the needs and cultural context of local communities, minimizing resistance, and promoting sustainability.Anthropology also offers a unique perspective on mental health and social stigma associated with certain illnesses. Anthropological research explores how pandemics can exacerbate mental stress and create new stigmas, as well as how societies respond and adapt to these changes.
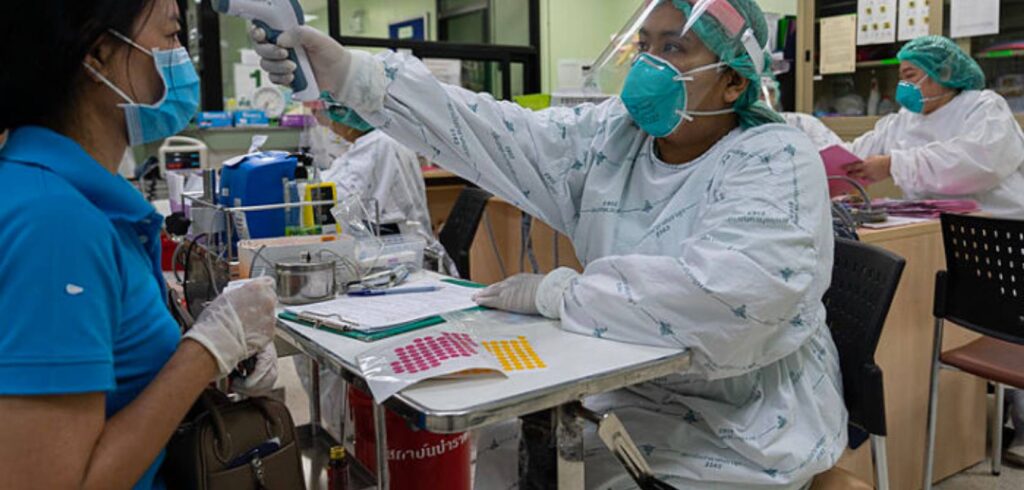

By incorporating these aspects, anthropology provides a rich insight into global health challenges. Viewing these issues through the lens of culture and society not only helps formulate more effective responses but also promotes a more humane and sustainable approach in facing global health crises. Engaging with anthropological perspectives is not just about understanding how diseases spread; it is about understanding how humans, as cultural beings, adapt and endure within it.